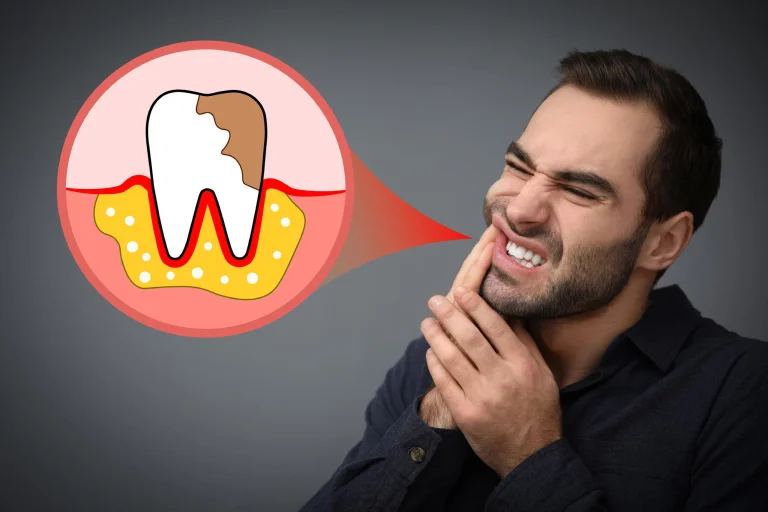
A tooth infection may start as something small, like a cavity or crack in the tooth, but it can quickly turn into a serious health problem if ignored. When germs get inside the tooth, they grow and cause swelling, pain, and pus. At first, the problem might just feel like a bad toothache, but if it’s left untreated, the infection can spread to the jaw, neck, and even the bloodstream.
The important thing to remember is that while tooth infections can be very dangerous, they are also very treatable if you act early. With modern dental care and antibiotics, most infections can be stopped before they spread. That’s why knowing the symptoms and getting quick treatment is the best way to stay safe and healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Tooth infections can become life-threatening if untreated, but with timely dental care, they are very manageable.
- Early signs include pain, swelling, bad taste in the mouth, and fever.
- A severe infection can spread to the jaw, neck, or even the bloodstream, leading to serious health complications.
- Dental visits, proper hygiene, and prompt treatment of cavities are the best prevention.
Understanding “How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You?”
A tooth infection starts when bacteria (tiny germs) sneak inside a tooth that has a cavity, crack, or other damage. Once inside, the bacteria grow and make pus (a thick, yellow liquid). This is what causes swelling, pain, and what dentists call an abscess.
At first, the infection might just hurt in your tooth or jaw. But if you don’t treat it, the bacteria don’t stay put—they can spread into your gums, jawbone, neck, or even travel through your blood to the rest of your body.
Now, many people ask, “How long until it becomes deadly?” The truth is:
- For some, it may take weeks or months before things get dangerous.
- But in rare cases, it can become very serious within just a few days.
It depends on how strong your immune system is, how fast the bacteria spread, and how quickly you get treatment. The good news is that if you go to a dentist or doctor, antibiotics and dental care can usually stop the infection early.
Symptoms of Tooth Infection
Spotting the signs early can save you a lot of pain and keep you safe. Here are common symptoms explained in simple words:
- Constant toothache or throbbing pain – The pain doesn’t go away, and it may pulse or beat like a heartbeat.
- Swelling in the face, cheek, or jaw – Your face might look puffy on one side.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods – Ice cream or hot tea may suddenly cause sharp pain.
- Bad taste or bad smell – If pus leaks from the tooth, it tastes bitter and gives you bad breath.
- Fever or feeling sick – Like when you’re coming down with the flu.
⚠️ If the infection spreads, the signs get much worse:
- You may find it hard to swallow food or water.
- You might have trouble breathing because of swelling.
- Your face or neck may swell so much that it looks different.
👉 These are emergencies. If that happens, don’t wait—go to the hospital right away.
Health Problems from Bad Tooth Infection
An untreated tooth infection can cause serious health problems that affect the whole body, not just your mouth. Some examples:
- Ludwig’s Angina – This is a dangerous infection under the tongue and jaw. It can swell so much that it blocks your throat, making it hard or impossible to breathe.
- Sepsis – If bacteria reach your blood, your whole body reacts. You may get fever, chills, a fast heartbeat, and confusion. Sepsis is life-threatening.
- Brain Abscess – In rare cases, the bacteria travel to the brain and cause swelling and pus pockets. This can lead to headaches, vision problems, or even seizures.
- Heart Infections (Endocarditis) – Bacteria from the tooth can travel through the blood and stick to the heart, infecting its inner lining.
These conditions are rare but extremely dangerous—and they show why it’s never safe to “wait out” a tooth infection.
Can You Die from a Tooth Infection?
Yes, it is possible. But it’s much less common today thanks to antibiotics and dentists.
In the past, before modern medicine, many people died from tooth infections. Today, the risk is low—as long as you get treated quickly.
If you wait too long, the infection may spread into areas that are harder to control, like the neck, chest, or brain. At that point, the situation can turn life-threatening.
👉 The lesson: Don’t ignore a tooth infection. Even if it starts small, it can turn into something very serious.
How Long Can a Cavity Go Untreated?
A cavity is the starting point for many tooth infections. Cavities don’t heal on their own, no matter how much you brush later. Let’s look at what usually happens:
- After a few months – The cavity eats through the enamel (the hard, white shell of the tooth). It then reaches the softer dentin inside.
- After about a year – The bacteria may reach the pulp (the center of the tooth where nerves and blood vessels live). That’s when infection and abscess begin.
- Over more time – The infection can spread deeper into the gums, bone, and other teeth, causing more pain and damage.
So yes, you can live with a cavity for months or years, but it’s like a ticking time bomb—the longer you wait, the bigger the risk of infection and serious problems.
Determinants of Severe Health Problems
Not everyone with a tooth infection will end up in the hospital. But some people have a much higher risk. Factors include:
- Weakened immune system – People with diabetes, HIV, cancer, or on chemotherapy can’t fight bacteria as strongly.
- Delaying treatment – Waiting too long allows bacteria to spread further.
- Location of infection – An infection in the upper teeth is closer to the brain. An infection in the lower teeth can spread toward the throat and neck.
- Overall health – If someone already has health issues (like heart disease or lung problems), their body struggles more with added infection.
This is why dentists sometimes treat tooth infections more urgently in people with existing health problems.
Preventing Tooth Infections
The great news is that tooth infections are mostly preventable! Here are easy habits that make a big difference:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste to clean away bacteria.
- Floss once a day to clean between teeth where food gets stuck.
- Visit your dentist regularly (every 6 months if possible) so small problems are caught before they become big ones.
- Treat cavities early—a simple filling is easier and cheaper than treating an abscess.
- Eat less sugar—bacteria love sugar, and it helps them make the acid that causes cavities.
👉 Think of it like this: Taking care of your teeth is not just about a pretty smile—it’s about keeping your whole body healthy.
Conclusion
Tooth infections may start as minor dental problems, but if ignored, they can become dangerous and, in rare cases, even fatal. While the timeline varies, an untreated infection can cause life-threatening health problems within days to weeks once it spreads.
The best approach is prevention through good oral hygiene and regular dental visits. If you notice symptoms such as swelling, severe pain, or fever, do not delay—see a dentist or doctor right away. Prompt treatment with antibiotics or dental procedures can stop the infection and protect your overall health.
FAQs
What are the common symptoms of a tooth infection?
Tooth pain, swelling in the face or gums, sensitivity, foul taste, and fever are common signs. Severe cases may cause difficulty swallowing or breathing.
How long does a tooth abscess last with antibiotics?
With proper antibiotics and dental treatment, symptoms usually improve within a few days. However, antibiotics alone are not a permanent cure. The infected tooth still needs dental treatment, such as a root canal or extraction.
How long until a tooth infection kills you?
There is no fixed timeline. In severe cases, life-threatening complications can appear within days if untreated. Most often, it takes weeks to months for an untreated infection to become deadly. Early treatment prevents this risk.
How can i prevent tooth infections?
Regular brushing, flossing, dental check-ups, and treating cavities early are the best ways to prevent infections.
What immediate treatments are available for a tooth infection?
Dentists may prescribe antibiotics, drain the abscess, perform a root canal, or extract the tooth. Painkillers can help manage discomfort, but only dental care removes the infection completely.